| Issue |
BIO Web Conf.
Volume 17, 2020
International Scientific-Practical Conference “Agriculture and Food Security: Technology, Innovation, Markets, Human Resources” (FIES 2019)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 00004 | |
| Number of page(s) | 5 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20201700004 | |
| Published online | 28 February 2020 | |
Small business as a factor in sustainable rural development
1
Ryazan branch (university) of Moscow Polytechnic University, 390046 Ryazan, Russia
2
Ryazan State University named after S.A. Yesenin, 390000 Ryazan, Russia
* Corresponding author: irina.litvinova2019@yandex.ru
Sustainable development of rural areas is a multifaceted and complex concept. One of the factors affecting the prosperity of the regions is the presence of small and medium-sized businesses. Improving government programs to support small and medium-sized businesses is a priority of state policy. The theoretical methodological and practical foundations of the strategic development of small and medium businesses were investigated. We have identified the main factors affecting the development of small business in Russia, such as low population density, low pre-emptive activity of the population, low support from the regional authorities. Creating an entrepreneurial environment is a priority to stimulate the development of small and medium-sized businesses.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2020
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
1 Introduction
Rural areas are designated as the most important resource of the country in the Sustainable Development Strategy of Rural Territories in the Russian Federation between now and the 2030 timeframe [1]. The priority of the sustainable development of rural areas is connected with systemic problem solving that has existed for many decades and were acutely manifested during the transition to a market economy in Russia. The 90s of the twentieth century were accompanied by a sharp drop in agricultural production and, as a result, a fall in the prestige of agricultural labor and an outflow of personnel, an increase in urbanization processes, a sharp decline in the living standards of the rural population, which was lagging behind the urban level before.
Sustainable development of rural areas is a complex and multidimensional problem, depending on the scale and instruments of state support, the existing potential and opportunities for self-development, which differ significantly (sometimes multiple) both by constituent entities, municipalities, and by rural settlements. The growth of the economy in the vast majority of rural settlements can be achieved by increasing the number and efficiency of small business [2].
2 Materials and methods
The research materials were statistical data for Russia and the Ryazan region, as well as regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation and the Ryazan region.
We have applied the empirical method, statistical and strategic analyzes.
Strategic analysis was chosen as the leading method of research, which made it possible to assess the potential of rural areas of the Ryazan region and the structure of the economy and to identify problems, opportunities and threats to rural development.
The process of strategic management in rural areas is cyclical in nature and is presented in Figure 1.
Strategic management is the consistent application of a number of methods (steps) to achieve the sustainable development goals of rural areas, such as:
conception;
strategy;
programming;
strategy implementation;
monitoring.
The initial stage of strategic management should be the development of a rural development strategy, which involves the definition of goals, objectives and subtasks, taking into account the needs of the population and enterprises located in this territory. It is also necessary to take into account the climatic conditions of the territory, the demographic factor, the socio-cultural and socio-economic conditions for the development of the rural territory.
The second stage is the strategy, which consists in modeling the development of the rural territory, taking into account the problems and development parameters of the budget of the rural settlement. At this stage, the selection of the optimal paths for the development of the rural area occurs. Also at this stage, key performance indicators for the implementation of the strategy should be identified.
The third stage is programming, that is, the construction of a specific mechanism for implementing the strategy, a set of specific measures included in the budget policy of a rural settlement.
The fourth stage is associated with the implementation of the strategy, which is done as a budget process in a rural settlement.
The fifth stage involves the analysis of the results obtained by monitoring the key indicators of the implementation of the strategy.
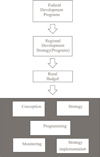 |
Fig. 1. Strategic management of rural areas |
3 Results and discussions
The purpose of the study is to assess the organizational and economic factors of small business development with the aim of enhancing the processes of self-development of rural settlements in the Ryazan region.
A large agricultural potential is concentrated on the territory of the Ryazan region; agricultural production in the regional economy plays a key role. The closest attention is paid to raising the level and quality of life of the rural population, the development of social infrastructure and engineering arrangement of rural settlements in our region.
In the Development Strategy of the Ryazan Region up to 2030 the development directions are:
creating a system of support and development of small farms, including personal subsidiary farms, peasant (farmer) farms, small agricultural organizations and consumer cooperatives;
implementation of projects aimed at the organization of cooperation aimed at small forms of management, an integrated approach from growing to processing and marketing of agricultural products.
In the Ryazan region, the subprogram “Sustainable development of rural territories” is being implemented under the program “Development of the agro-industrial complex” [3]. The goal of the subprogram is to create comfortable living conditions in rural areas.
Funds allocated for the implementation of the subprogram “Sustainable development of rural areas” are presented in Table 1.
The financing program have increased by 55.6 million rubles compared to those in 2018 with 2015, which amounted to 22.67%.
In addition, funding from the federal budget decreased by 10.3 million rubles, that is 7.94%. The share of the regional budget increased from 47.09% in 2015 to 60.29% in 2018. The increase in regional financing amounted to 65.9 million rubles that is 57.06%. In such a way, we can conclude that this program is a priority for the Ryazan region and its development clearly corresponds to the strategic objectives of the regional government.
Small forms of management in the agrarian and industrial complex of the Ryazan region are represented by peasant (farmer) farms, agricultural consumer cooperatives of various kinds, and personal subsidiary farms of citizens.
The All-Russian Agricultural Census [4] was in 2016, conducted on the basis of the Federal Law of July 21, 2005 No. 108 “On the All-Russian Agricultural Census” (ARAC). The last all-Russian agricultural census was held in 2006. The results are presented in Table 2.
The number of small enterprises areas has decreased significantly in rural according to the All-Russian Agricultural Census. The number of agricultural enterprises was only 33.9 percent in 2016. However, the cultivated area increased by 23.64 percent. There has been an enlargement of agricultural enterprises of the Ryazan region in 10 years. The number of medium and large enterprises decreased in 2016 and amounted to 65.8 percent. However, the area of land they cultivated increased by 36.6 percent.
There is other trend for small agricultural enterprises. There was a 3-time reduction in their number, and the cultivated area decreased 2 times. This suggests that state support for small and medium agricultural businesses in the Ryazan region is not sufficient. A set of measures aimed at improving the financial sustainability of small agricultural producers is needed. The number of subsidiary agricultural enterprises has also decreased by almost 10 times, but the area they have cultivated has increased 30 times. The transition of personal subsidiary farms to the small business category is the growth potential of this industry. Peasant (farmer) farms for the study period 2006–2016 declined slightly, by 6.8 percent, and the area they cultivated increased 1.8 times.
The number of personal subsidiary and individual farms of citizens decreased by 14.9 percent, and the area they cultivated increased by 25 percent. The number of non-profit associations of citizens decreased by 5.6 percent, and the area they treat was also reduced by 1.96 percent. Thus, there is the enlargement of agricultural producers and a reduction in the number of small farms.
Currently, the following factors hinder the development of the small business sector [5]:
difficulty in finding consumers of products;
instability of the regulatory framework governing the business;
a high level of taxation of small and medium-sized entrepreneurs;
high administrative barriers and violation of the rights of entrepreneurs by regulating authorities;
unavailability of borrowed funds for small and medium-sized businesses.
An important factor hindering the development of small business in the rural areas of the Ryazan region is the spatial differentiation of the population. More than 48% of the total population of the region lives on the territory of Ryazan. Over the past 10 years there has been a tendency to reduce the rural population and the migration of rural residents to the cities. In addition to Ryazan, population growth occurs in Rybnoye, Aleksandro-Nevsky and Kadoma districts. Higher real incomes of the population in cities determine migration flows. The disparity between the average wage of urban and rural population is 12%
The formation of the business environment is main task of the Ryazan region government in rural areas. The business environment is a combination of public institutions and conditions, legal norms, and state support systems. It is also a certain social climate, security conditions, a special infrastructure for entrepreneurship, that everything ensures the formation and further development of entrepreneurship [6].
The Federal Law “On the Development of Small and Medium Business in the Territory of the Russian Federation” is the statutory and legal basis for the functioning of small and medium business entities in the Russian Federation.
Currently, a variety of measures and initiatives is implemented to stimulate the development of the small and medium-sized enterprise sector at the federal level. As a result, the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation implements the following programs of state support for projects through the JSC “SME Corporation” [7], presented in Table 3.
“The roadmaps” of the national entrepreneurial initiative were implemented at the federal level, which contain specific measures to improve the business environment.
The Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation actively promotes a program of concessional lending to SMEs. The small and medium-sized entrepreneurs offer the rate in authorized banks of up to 8.5%.
The federal initiatives are not always supported at the regional level because the regional budgets filling is insufficient. The State program “Economic Development in 2015–2020” [8] operates in the Ryazan Region, approved by Resolution of the Government of the Ryazan Region of October 29, 2014 No. 306.
This program is specified in 5 subprograms:
“Increasing investment potential”;
“Development of small and medium enterprises”;
“Improving the provision of state and municipal services”;
“Ensuring the implementation of the Program”;
“Trade development”.
Figure 2 shows the planned figures for the amount of funding for the program “Economic Development of the Ryazan Region in 2015–2020. The federal budget fund was increased in 2016–2017, while the level of regional finance varied insignificantly. The financing of this program was spent in the amount of 252.264 million rubles in 2015, of which the subprogram “Improving the delivery of state and municipal services” was 199.561million rubles. The financing of this state program amounted to 543.310 million rubles in 2016, of which financing for the subprogram “Increasing investment potential and export development» was 27.794 million rubles, the financing of the subprogram “development of small and medium enterprises” was 116.883 million rubles. The financing of this state program was 555 million rubles in 2017. The sub-program “Increasing investment potential” was 2,794 million rubles in 2017. The financing of this program was 676.153 million rubles in 2018, the subprogram “development of investment potential” cost 187.884 million rubles.
Thus, the planned funding is insufficient for the implementation of all subprogrammes at the same time.
As part of the implementation of the subprogram “Development of small and medium-sized businesses”, the Regulations on the organization and conduct of competitive selection of small and medium-sized businesses, organizations that form the infrastructure to support small and medium-sized businesses in the Ryazan region, and municipal units of the Ryazan region were approved to receive subsidies from the regional budget and (or) federal budgets.
The Decree of the Government of the Ryazan Region of April 23, 2015 N 92 “On Approval of the Procedures for Granting Subsidies for the Activities of the Small and Medium-Sized Businesses Subprogramme” and medium entrepreneurship is valid.
Also, within the framework of the implementation of the subprogram “Improving the provision of state and municipal services”, 29 offices of multifunctional centers were created, 5 of them in Ryazan. Offices of multifunctional centers “My Documents” are geographically located in each center of the region, and in total provide access to public services for just over 1.1 million people [9].
Through the Internet portal “State Services” remote access to the Personal Account of an individual entrepreneur is provided, you can issue a building permit, submit information on voluntary certification, get advice on taxes and more.
As part of the “Increasing investment potential” subprogram, the Investment Portal of the Ryazan Region was created, within which the investment map of the Ryazan Region operates, the Investment Council of the Ryazan Region is organized, an investment strategy and declaration are developed, and industrial parks are being created. The Development Corporation of the Ryazan Region functions, which accompanies investment projects at all stages of development, provides legal assistance to investors, provides infrastructure and resources, and protects the rights of investors [10].
The amount of financing of the subprogram “Sustainable development of rural territories”, million rubles.
The number and total area of land according to the results of the All-Russian Agricultural Censuses 2006 and 2016
Federal programs to support small and medium businesses.
 |
Fig. 2. The planned growth rates of financing of the State program of the Ryazan region “Economic development in 2015–2020”, % |
4 Conclusion
Ensuring the sustainable development of rural areas is one of the priorities of the socio-economic development of Russia, as evidenced by the adopted legal acts. Under the conditions of the economic crisis, an increase in the scale of state support for the development of rural areas is problematic, which dictates the need to find opportunities for the self-development of each rural settlement and municipal district. This opportunity consists in activating small business, the development of which is hampered by difficulties in attracting resources, administrative barriers, and the lack of knowledge and experience among rural residents. For small agribusiness, an institutional environment should be created in which the wholesale distribution system is currently the weak link [11].
The overwhelming majority of domestic farmers face difficulties in marketing their products, even under counter-sanctions, reducing imports for many food groups and government-implemented import substitution measures. The authors evaluated the problems of sales of products of small forms of management and their solutions.
Regional programs for the development of small and medium enterprises should be coordinated with federal programs for expanding the financing of small businesses [12].
Regional authorities should develop measures to stimulate innovative activity of small and medium-sized businesses, create business incubators, prototyping centers, industrial clusters and other elements of the infrastructure of the business environment. It is necessary to work with the banking sector in the region to create conditions for lending to small and medium businesses.
References
- Strategy of social and economic development of the Ryazan region until 2030, Project, 109-112. Retrieved from: https://mineconom.ryazangov.ru/direction/economy/proekt_strategii.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Website of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation, retrieved from: http://economy.gov.ru/minec/main-12-18. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Food of the Ryazan Region, retrieved from: https://www.ryazagro.ru/-6 [Google Scholar]
- The site of the All-Russian Agricultural Census (2016) Retrieved from: http://www.vshp2016.ru/-105-110 [Google Scholar]
- V.O. Betin, Small business development in the region, thesis. Retrieved from: https://www.dissercat.com/content/razvitie-malogo-predprinimatelstva-v-regione-5-6. [Google Scholar]
- I.V. Litvinova, Formation of programs for the socio-economic development of rural areas, thesis. Retrieved from: http://www.dslib.net/economika-xoziajstva/formirovanie-programm-socialno-jeko-nomicheskogo-razvitija-selskih-territorij.html-20-30. [Google Scholar]
- The site of the Corporation SME, retrieved from: https://corpmsp.ru/-15-25. [Google Scholar]
- Website of the Ministry of Industry and Economic Development of the Ryazan Region, retrieved from: https://mineconom.ryazangov.ru/?utm_ referrer=yp.ru&utm_source=yp.ru-18-25. [Google Scholar]
- M.N. Salomatina, Improving the management of the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the field of waste management, thesis, 63–65. Retrieved from: http://www.dslib.net/economika-xoziajstva/sovershenstvovanie-processa-upravlenija-razvitiem-malogo-i-srednego.html [Google Scholar]
- Investment portal of the Ryazan region, retrieved from: http://invest-r.ru/articles/details/id/30- [Google Scholar]
- A.V. Myadzelets, Role of territorial remoteness, economic and social factors in development of Siberian and northern regions of Russia, IOP Conf. ser. Earth and environmental sci., 40–45, (2018) [Google Scholar]
- N.V. Bogdanov, G.B. Dugarova, Roadside service as factor of regional development, IOP Conf. ser. Earth and environmental sci., 110–118 (2018) [Google Scholar]
All Tables
The amount of financing of the subprogram “Sustainable development of rural territories”, million rubles.
The number and total area of land according to the results of the All-Russian Agricultural Censuses 2006 and 2016
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1. Strategic management of rural areas |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 2. The planned growth rates of financing of the State program of the Ryazan region “Economic development in 2015–2020”, % |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



