| Issue |
BIO Web Conf.
Volume 30, 2021
II International Symposium “Innovations in Life Sciences” (ILS 2020)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 02002 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Sorbents – As Factors of Quality of Life and Health | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20213002002 | |
| Published online | 22 April 2021 | |
Coordinating metal Mn2+ and Ni2+ compounds with acetylsalicylic acid: the influence on the cardiorespiratory system
1
V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, 295007 Simferopol, Russia
2
Institute of Foreign Philology, V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, 295007 Simferopol, Russia
* Corresponding author: elena-chuyan@rambler.ru
The paper researches the effect of manganese (АCMn2+) and nickel (АCNi2+) acetylsalicylates in doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg on the characteristics of the rats’ cardiorespiratory system. It is ascertained that coordinating metal compounds with the acetylsalicylic acid have a more pronounced biological effect in comparison with a monocompound of the acetylsalicylic acid; this makes the further search for coordinating compounds’ effects more promising.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2021
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
1 Introduction
A widespread problem of modern society is human pathologies connected with the functioning of different elements of cardiovascular system; this predetermines the necessity of searching for new effective substances and of studying their activity mechanism. The representatives of non-narcotic analgesics – the salicylates, namely the well-known acetylsalicylic acid, can be a relatively safe remedy [1, 2]. Currently, the creation of new pharmaceutical dosage forms and remedies on the basis of the acetylsalicylic acid, being deprived its side effects, is an important area of the modern bioorganic and pharmaceutical chemistry and of biomedicine in general [3, 4]. The leading role in this area is played by new derivatives of the acetylsalicylic and salicylic acids, and by the compounds, obtained on their basis, with different biologically active molecules and metals [3], for instance, with Mn2+ and Ni2+. Such compounds are synthesized by the Department of General and Organic Chemistry of V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University under the supervision of Professor A. N. Gusev; a range of these compounds’ chemical properties and some biological effects were studied [2]. However, the research of these compounds’ influence on the cardiorespiratory system has not been carried out yet. It is necessary to mention that important characteristics of the functional state of the whole cardiorespiratory system and the cardiac performance at a definite period of time and ones of the main oldest biomarkers of the body state on the whole are a heart rate (HR), a respiratory rate (RR), a systolic blood pressure (SBP) and a diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
2 Experimental
All the researches on the animals were carried out according to the principles set out in Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the EU Council of 22.09.2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes.
Healthy sexually mature male laboratory Wistar rats, weighing 180-200 gr (“FSUE “Nursery of laboratory animals “Rappolovo”) and having been placed under quarantine not less than for 14 days, were selected for the experiment. The experiments were performed on 70 male rats, characterized by an average motor activity and low emotionality in the “open field” test, and which make up the majority of the population; that is why they develop the most typical reaction to the effect of different factors [5], including the tested chemical compounds.
The animals were kept under standard conditions of the vivarium at the temperature of 18–22°C on the bedding «Rexofix МК 2000» (on the basis of ear shanks) with the natural 12-hour day-and-night cycle, with free access to water (State Standard 33215-2014 «The handbook of keeping and nursing laboratory animals. The regulation rules on housing equipment and procedure organization»), and to full-fledged granulated food of State Standard Р-50258-92.
The research was carried out at the Centre for Collective Use of Scientific Equipment “Experimental Physiology and Biophysics” of the Department of Human and Animal Physiology and Biophysics of V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University.
Design of studies on the reaction of the cardiorespiratory system to the Introduction of the tested compounds, the used research and statistical methods.
The synthesis, the research of the composition, structure and properties of the coordinating compounds of the acetylsalicylates with nickel (АCNi2+) and manganese (АCMn2+) were done at the Department of General and Organic Chemistry of V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University under the supervision of Professor A. N. Gusev.
The research of the biological effect of the acetylsalicylic acid, АCNi2+ and АCMn2+ was carried out during their intraperitoneal injection into rats in the doses of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg. For this purpose, the rats were divided into 7 groups (10 rats in each group):
group 1 is a biological control (К, n=10), they are the animals which were injected by the physiological solution of 0.9 % in the volume of 0.2 ml;
groups 2 – 3 are the animals which were injected by the acetylsalicylic acid in the doses of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively (n=10), the volume of 0.2 ml;
groups 4 – 5 are the animals which were injected by АCNi2+ in the doses of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively (n=10), the volume of 0.2 ml;
groups 6 – 7 are the animals which were injected by АCMn2+ in the doses of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively (n=10), the volume of 0.2 ml.
The bioscreening of the acetylsalicylates was done 20 minutes later after the intraperitoneal injection in the stated concentrations, as at this period the maximum concentration of the acetylsalicylic acid is observed [6]. Simultaneously the following characteristics of all the groups’ animals were registered: heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
BP, HR and RR of the rats were registered with the help of the system NIBP200A («BiopacSystems, Inc.», USA). BP and HR were registered on the tail artery by applying the cuff on the tail base. In order to record RR the sensor was fixed on the chest area. While registering the indices, the animals were put into an individual box and were carried to the chamber Biopac with a constantly kept temperature of 33°C for creation of comfortable conditions for the animal.
The record of the indices was done during 5 minutes from the moment of the sensor’s signals stabilization.
This time is enough for the five-fold BP measurement; HR and RR were being registered continuously. The record and the data processing were done by the computer with the help of the software program «AcqKnowledge 4.2 for MP150» (Fig. 1).
The data of three repeated experiments were used for the statistical manipulation. The non-parametric statistic methods were applied as the distribution of variate values differed from the normal. The calculations, the statistical manipulation and graphic design of the obtained in the research data on the effect of the tested compounds on the physiological characteristics were done by using the program Microsoft Excel and the program package StatSoft STATISTICA 8. The reliability of the statistic differences between the control group (intraperitoneal injection of the physiological solution) and experimental groups with different doses of injecting the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates Ni2+, Mn2+ was assessed by Mann-Whitney test.
3 Result and discussion
It was found out that the animals of the control group, after being injected by the physiological solution, did not demonstrate reliable changes of the cardiorespiratory system characteristics (Table 1). At the same time the reliable lowering of HR by 12 % (p≤0.05) in animals, being injected by the acetylsalicylic acid in the dose of 5 mg/kg, was registered; however, at the increase of the injected dose up to 10 mg/kg the lowering of HR was less considerable – by 8% (p≤0.05).
The reaction of the cardiorespiratory system to the Introduction of the coordinating compounds АCNi2+ and АCMn2+ differed from the reaction to the Introduction of the acetylsalicylic acid.
The most pronounced changes of the cardiorespiratory system characteristics were observed in the rats being injected with АCMn2+. Thus, in contrast to the acetylsalicylic acid, the Introduction of АCMn2+ in the dose of 5 mg/kg led to a reliable growth of HR by 5 % (p≤0.05). Besides, a reliable growth of DBP by 5 % (p≤0.05) and of RR by 15 % (p≤0.05) was observed as regards to the characteristics in the animal control group (see Table 1).
The increase of the АCMn2+ dose up to 10 mg/kg led to the growth of HR by 7 % (p≤0.05), however, in contrast in a dose of 5 mg/kg with the help of the software program «AcqKnowledge 4.2 for MP150» to АCMn2+ in the dose, there was the lowering of RR by 14 % (p≤0.05) as regards to the characteristics in the animal control group. The rest of the characteristics did not change reliably (see Tables 1, Fig. 1).
The increase of the АCMn2+ dose up to 10 mg/kg led to the growth of HR by 7 % (p≤0.05), however, in contrast to АCMn2+ in the dose, there was the lowering of RR by 14 % (p≤0.05) as regards to the characteristics in the animal control group. The rest of the characteristics did not change reliably (see Tables 1, Fig. 1).
At the Introduction of АCNi2+ in the dose of 5 mg/kg there was the lowering of RR by 15.1 % (p≤0.05) in comparison with the RR in the animal control group; with the increase of this compound dose up to 10 mg/kg the directivity of animals’ cardiorespiratory system reaction to the Introduction of АCNi2+ remained identical to the same as at the Introduction of 5 mg/kg dose: RR lowered by 14% (p≤0.05) in comparison with RR in the animal control group. The rest of the characteristics did not change reliably (see Tables 1, Fig. 1).
Thus, the intraperitoneal Introduction of the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates Mn2+ and Ni2+ led to the changes of laboratory animals’ cardiorespiratory system functioning. The acetylsalicylic acid had a bradycardia effect in all the tested doses. The inclusion of the metal Ni2+ into the acetylsalicylic acid molecule structure led to the onset of bradypnoea but levelled the bradycardia effect. The inclusion of Mn2+ into the acetylsalicylic acid molecule had the most significant effect; it was evidenced in the stimulation of the cardiorespiratory system (in the dose of 5 mg/kg): DBP, HR and RR increased, however, at the dose of 10 mg/kg tachycardia enhanced insignificantly, and tachypnea was changed by bradypnoea.
We may conclude that the acetylsalicylic acid molecule modification results in the changes of the effects of the initial compound and in the emergence of new characteristics
Actually, the analysis of the coordinating compounds АCMn2+ and АCNi2+ efficiency regarding the acetylsalicylic acid showed (Fig. 2) that the maximum changes of the cardiorespiratory system indices were registered at the modification of the acetylsalicylic acid by metal Mn2+, as at the Introduction of АCMn2+ in the dose of 5 mg/kg the animals increased reliably RR by 14.7% (p≤0.05) and DBP by 7.1 % (p≤0.05) as regards to the indices in the animal group which was injected by the acetylsalicylic acid in this dose.
At the Introduction of АCNi2+ in the dose of 5 mg/kg only DBP increased reliably by 4 % (p≤0.05) as regards to the indices in the animal group which was injected by the acetylsalicylic acid. The rest of the cardiorespiratory system characteristics in the animal groups 4 – 7 regarding the group of animals injected by the acetylsalicylic acid were not observed.
 |
Fig. 1. The example of the recording of cardiovascular system indices of the rats’ BP, HR and RR under the effect of АCNi2+ in a dose of 5 mg/kg with the help of the software program «AcqKnowledge 4.2 for MP150» |
The characteristics of the rats cardiorespiratory system after injecting the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates of Ni2+ and Mn2+ in different concentrations
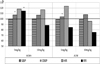 |
Fig. 2. The characteristics of the cardiorespiratory systems of animals, injected by the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates of Mn2+and Ni2+ in concentrations of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg relatively to the values in the group of animals, injected by the acetylsalicylic acid, and taken as 100 %. |
4 Conclusion
On the whole, the results of this research allowed ascertaining that the acetylsalicylic acid complexing with such metals as nickel and manganese improve the efficiency of newly synthesized acetylsalicylates since АCNi2+ and АCMn2+ have a more pronounced effect on the cardiorespiratory system of the animals in comparison with the acetylsalicylic acid. The manifestation of the more pronounced effects of metal acetylsalicylates in comparison with the acetylsalicylic acid is presented in the researches of Z. Chohan and coauthors on the kaolin model of the rats’ inflammation, and in the modelling of the rats’ acute myocardial infarction [7].
Our researches show that the compounds АCNi2+ and АCMn2+ demonstrate some new properties which are not typical of the acetylsalicylic acid. Probably, the obtained in this research effects of the acetylsalicylic acid with transition metals Ni2+ and Mn2+ may be connected with their ability to interact with metalloenzymes, as it is shown in [7], and/or with their ability to change the activity of a number including arginase, of enzymes [8,9,10], superoxide dismutase-1, glutathione peroxidase-4, NA+/K+-ATPase [11], and, thus, to inhibit proinflammatory prostanoids and intensify the activity of antioxidant enzymes [11].
Thus, the acetylsalicylates of nickel and manganese show biological properties which can be of a specific interest in the process of treating a number of cardiorespiratory system diseases; this makes the further search for biological and pharmaceutical activity of these coordinating compounds promising. Since the compounds АCNi2+ and АCMn2+ have qualitatively and quantitatively effects different from such of the acetylsalicylic acid, then the further research of the salicylic acid derivatives can solve the problem of the side effects, increase the therapeutic potential of the initial compound for the creation of new effective compounds on their basis.
Acknowledgment
The reported study was funded by RFBR, project number № 20-33-70142 on the experimental equipment of the Center for Collective Use of Scientific Equipment “Experimental Physiology and Biophysics” of the Department of Human and Animal Physiology and Biophysics of Taurida Academy (structural division) of V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University
References
- A.G. Gilman, Practice, 4, p. 336 (2006) [Google Scholar]
- I. V. Cheretaev, D. R. Khusainov., I. I. Koreniuk, Young Scientist, 10, 485-491, (2015) [Google Scholar]
- A. S. Grigorieva, Trace elements in medicine, 1, 17-22, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- K. Bica, C. Rijksen, M. Nieuwenhuyzena [et al.], Phys. Chem, 12, 2011-2017 (2010) [Google Scholar]
- I V. Cheretaev, M. Yu. Ravaeva, E. R Dzheldubaeva, E. N. Chuyan, V. F. Shulgin, N. Sheichmambetov, M.V. Palaevskaya, Scientific notes of the Crimean Federal University named after Vernadsky. Biology, Chemistry, 5, 204-206 (2019) [Google Scholar]
All Tables
The characteristics of the rats cardiorespiratory system after injecting the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates of Ni2+ and Mn2+ in different concentrations
All Figures
 |
Fig. 1. The example of the recording of cardiovascular system indices of the rats’ BP, HR and RR under the effect of АCNi2+ in a dose of 5 mg/kg with the help of the software program «AcqKnowledge 4.2 for MP150» |
| In the text | |
 |
Fig. 2. The characteristics of the cardiorespiratory systems of animals, injected by the acetylsalicylic acid and acetylsalicylates of Mn2+and Ni2+ in concentrations of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg relatively to the values in the group of animals, injected by the acetylsalicylic acid, and taken as 100 %. |
| In the text | |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



